Most people don’t want to “learn” an AI tool. They want it to help—and to do so clearly, quickly, and without a struggle. A few tools understand that. Others seem built for engineers, not everyday users.This article draws a clear line between the two. You’ll see seven AI tools that succeed because they respect your time and seven experiences that fall short due to clumsy design or unclear structure. Each entry reflects what real users have reported after trying to work with—or failing to—use these tools.We begin with the most user-friendly AI tools, the ones that feel helpful from the start.
ChatGPT

ChatGPT adapts to user input with minimal friction. As of June 2025, it serves approximately 800 million weekly active users (OpenAI). GPT-4 expands capabilities with tools like file uploads and browsing. Custom Instructions refine tone and response style, which allows users to shape how the assistant communicates within each session.
Perplexity AI
Perplexity usage increased by 400% in 2023, attracting users who prioritize clarity and fact-based answers. Copilot enhances question framing, while inline citations ensure transparency of sources. Its integration of verified search with conversational AI has made it a trusted tool for researchers and everyday users seeking reliable information.
Bolt
Bolt lets users build polished websites without needing to code. From layout to branding and SEO, its AI handles the details while creators focus on content. Sites can be launched in hours. So, it’s especially popular among solo business owners who need speed and simplicity without relying on developers.
Claude
Claude 3 Opus processes dense documents—such as contracts and PDFs—into clear summaries. Its calm tone and structured responses further support professional users who rely on consistent reasoning. Developed by Anthropic, Claude emphasizes safety and clarity while utilizing long-term memory to manage complex inputs that require careful interpretation and produce focused, accurate outputs.
Canva Magic Studio

With over 170 million users, Canva serves the daily needs of education and small businesses. Its Magic Studio tools, including Magic Write and Beat Sync, enable the quick creation of graphics and presentations. No design background is required, which makes it possible for anyone to produce polished content in minutes with AI support.
Google Gemini
Originally rebranded from Bard in 2023, Gemini now integrates across Gmail, Docs, Android, and Maps. It also handles voice and image input with ease. Built on the Gemini 1.5 architecture, the app adds context awareness and multimodal fluency to support a wide range of everyday digital interactions without extra steps.
Runway ML
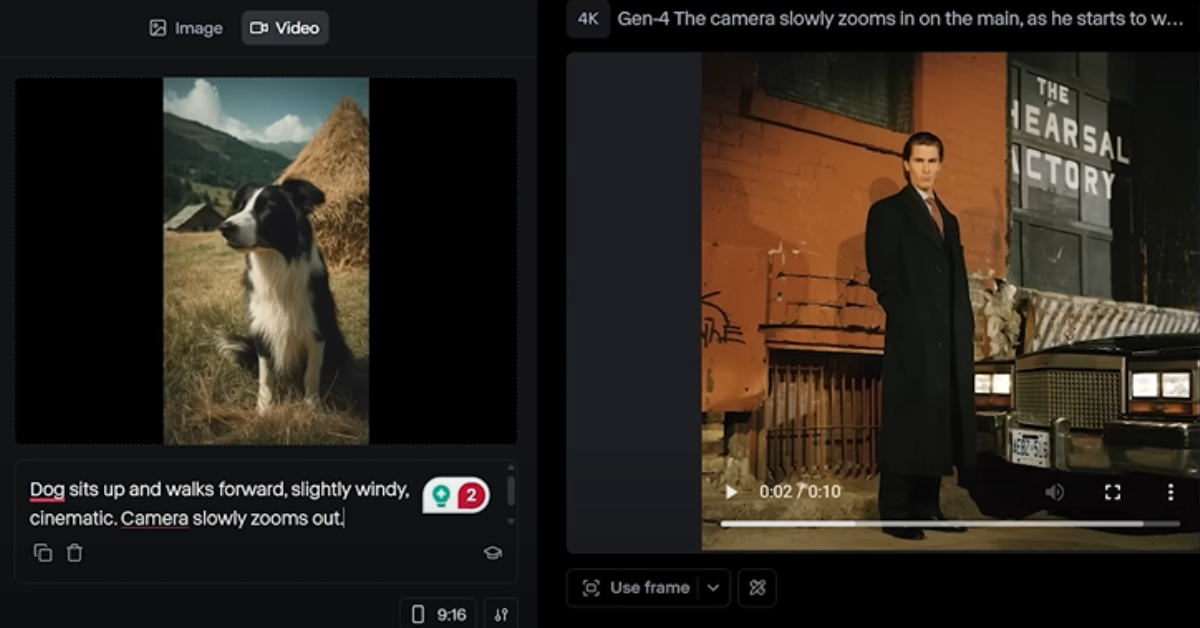
Runway supports storytelling by giving users control at every step. Its drag-and-drop timeline resembles pro editing tools like Final Cut. Prompts even transform into vivid visuals using the Gen-2 model. Creators can animate or adjust scenes without complex setups. However, not all AI tools keep it simple—these next seven trip users up with confusing design and steep learning curves.
Multimodal Developer Tools
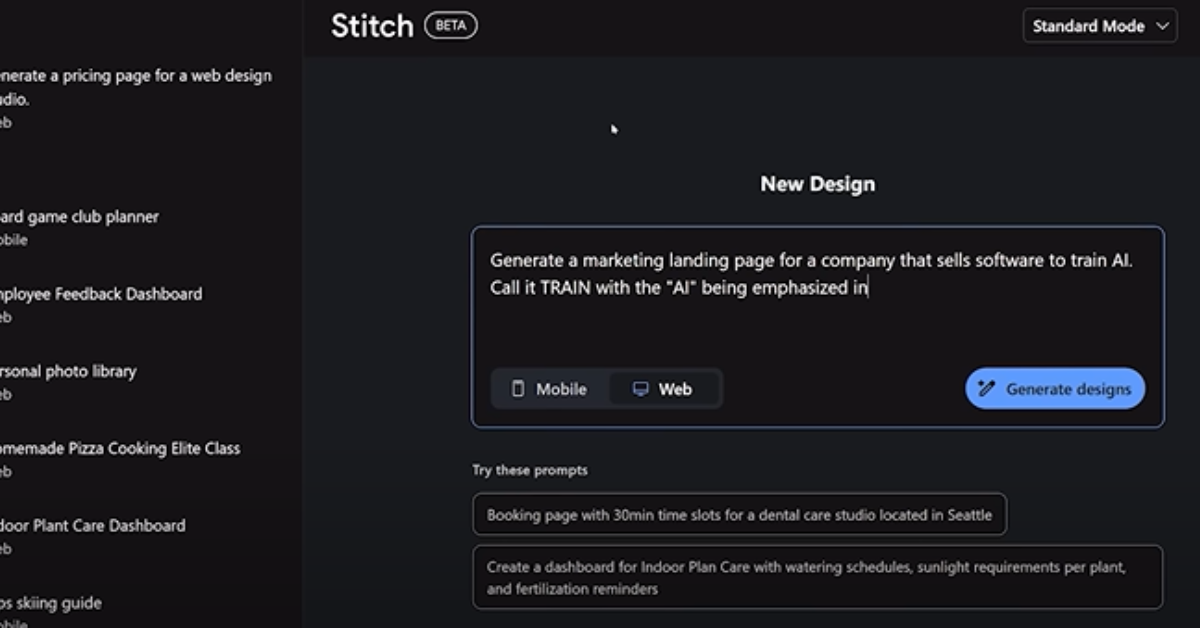
They sound accessible at first. But platforms like Google Stitch are made for developers, not casual users. While they allow UI generation from text and image inputs, they require deep familiarity with APIs and routing logic. Documentation is developer-oriented, which leaves non-coders confused by the lack of visual guidance or structured onboarding.
LLM Browser Assistants
Tools like Arc Sidebar and Comet promise live summarization and tab memory, yet they rarely behave consistently. Mid-task resets are common, and context often slips between pages. These features are still in open beta, and user feedback repeatedly highlights glitches that make these assistants more challenging to use than advertised.
ComfyUI
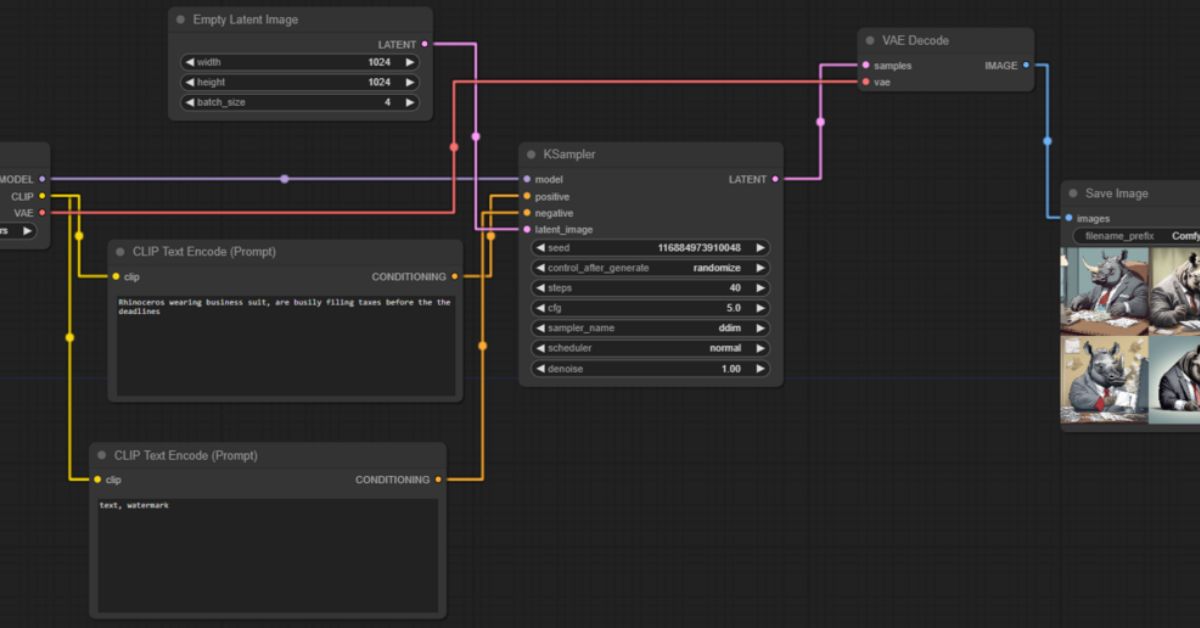
Success with ComfyUI depends on connecting nodes in the correct order, though no official guidance clearly explains how. Beginners often struggle to generate anything meaningful. The interface offers endless options, but trial and error dominate the learning curve. For most users, the potential remains out of reach rather than within grasp.
Luminar Neo
Luminar Neo draws users in with sleek visuals and smart tools like Sky AI. However, the experience sometimes proves challenging due to limited direction and complex layer behavior. Its intuitive appearance contrasts with a workflow better suited to those with editing experience.
Automatic1111
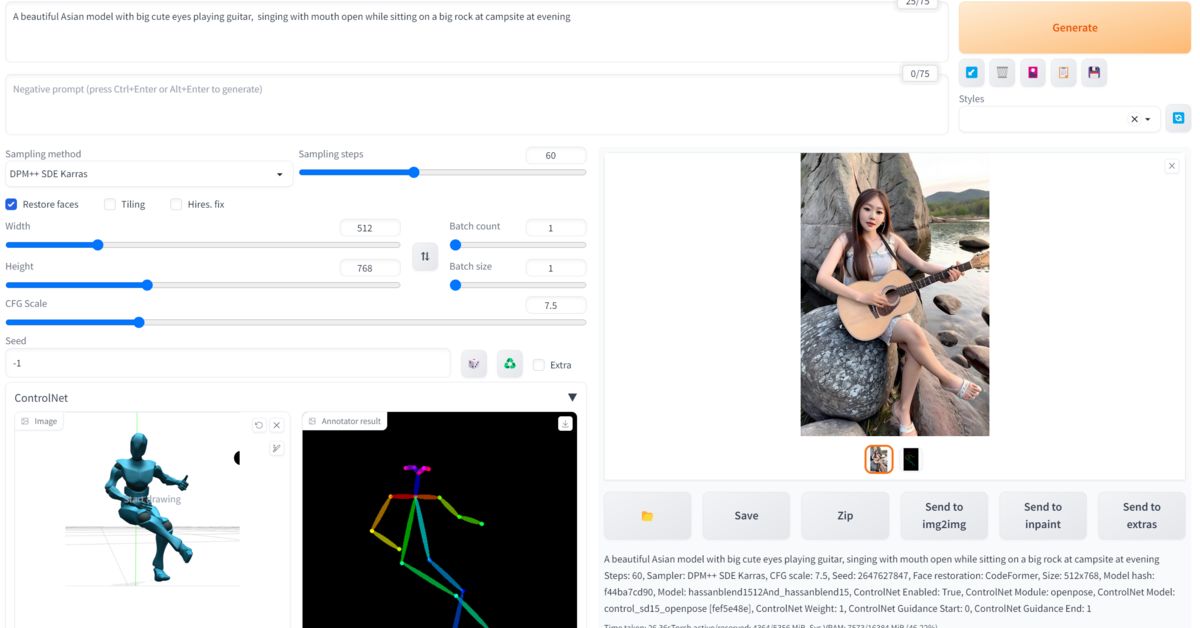
Running locally, Automatic1111 opens powerful possibilities for image generation. Yet its installation process—requiring Python setup and CLI navigation—filters out most newcomers. The UI itself is compact and overstuffed. Plus, troubleshooting depends heavily on community forums or GitHub, where solutions vary in reliability and clarity.
AI Agents

To function appropriately, autonomous AI agents like AutoGPT and Mariner require API keys and monitoring of recursive logic. Logs often lack clarity, and outcomes are unpredictable. Although they aim to automate entire workflows, these systems frequently stall mid-task, which leaves users puzzled by incomplete executions and limited transparency.
Intuitive AI Prototypes

These tools are described as “intuitive,” yet their design contradicts this label. Research prototypes rely on unexplained terms like “embedding” and “latent space.” Undo functions and error handling are absent. Without built-in guidance, even experienced users struggle to navigate interfaces or understand how to achieve meaningful results.